PROJECT: Concrete Dam Structure / cracking EVALUATION
SCOPE OF WORK: Forensic Investigation / Materials Evaluation / Repair Recommendation
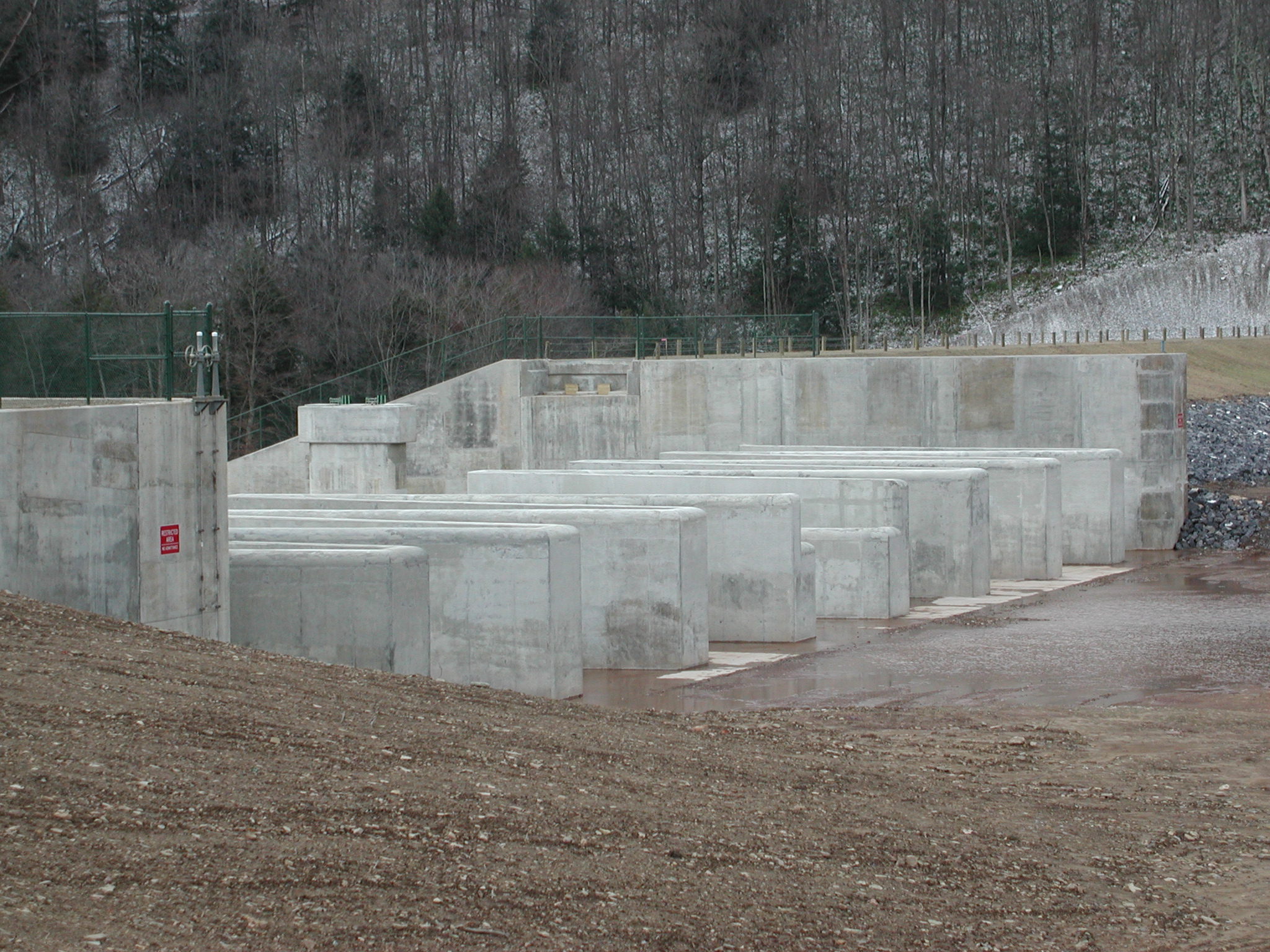
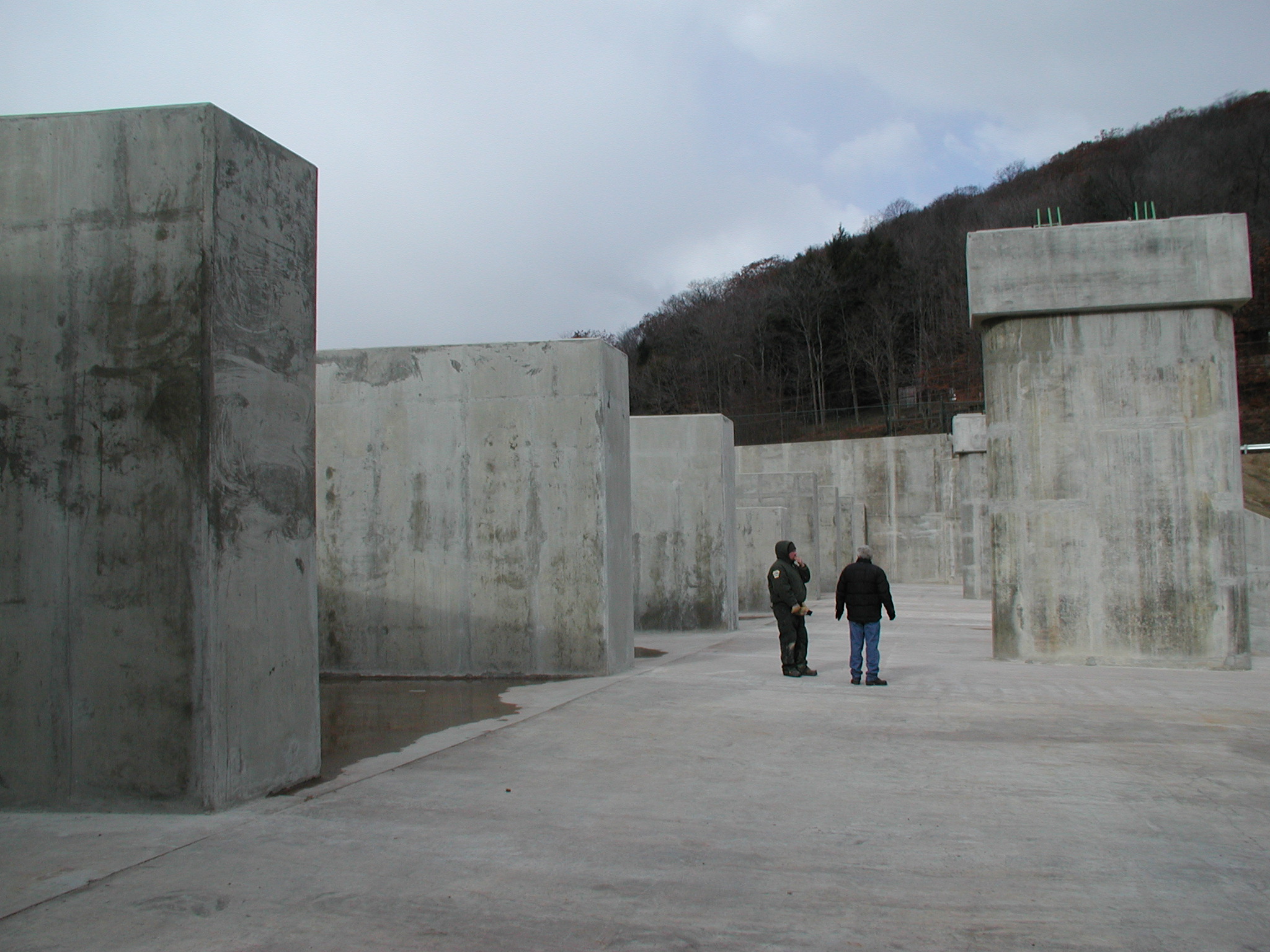
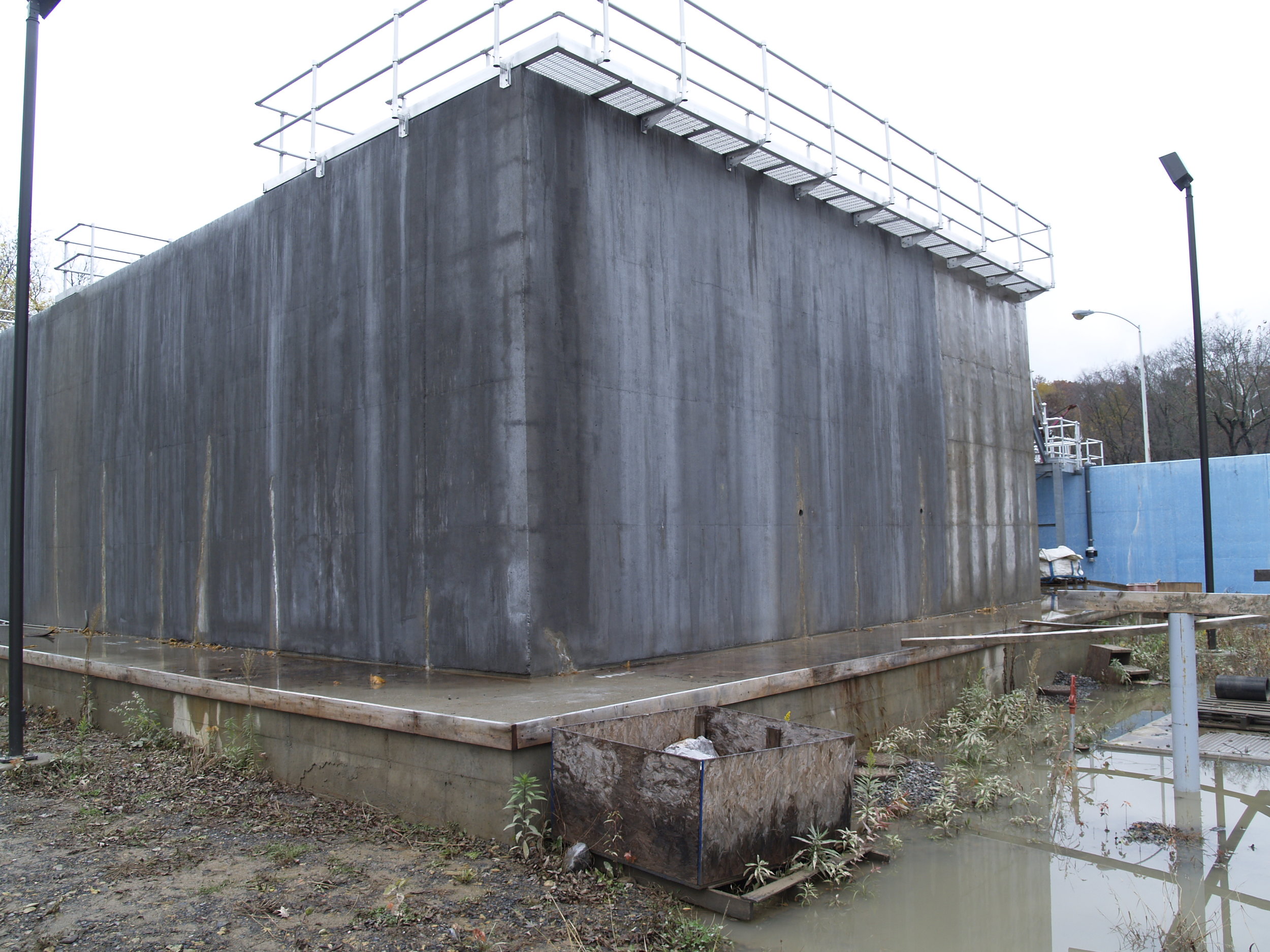
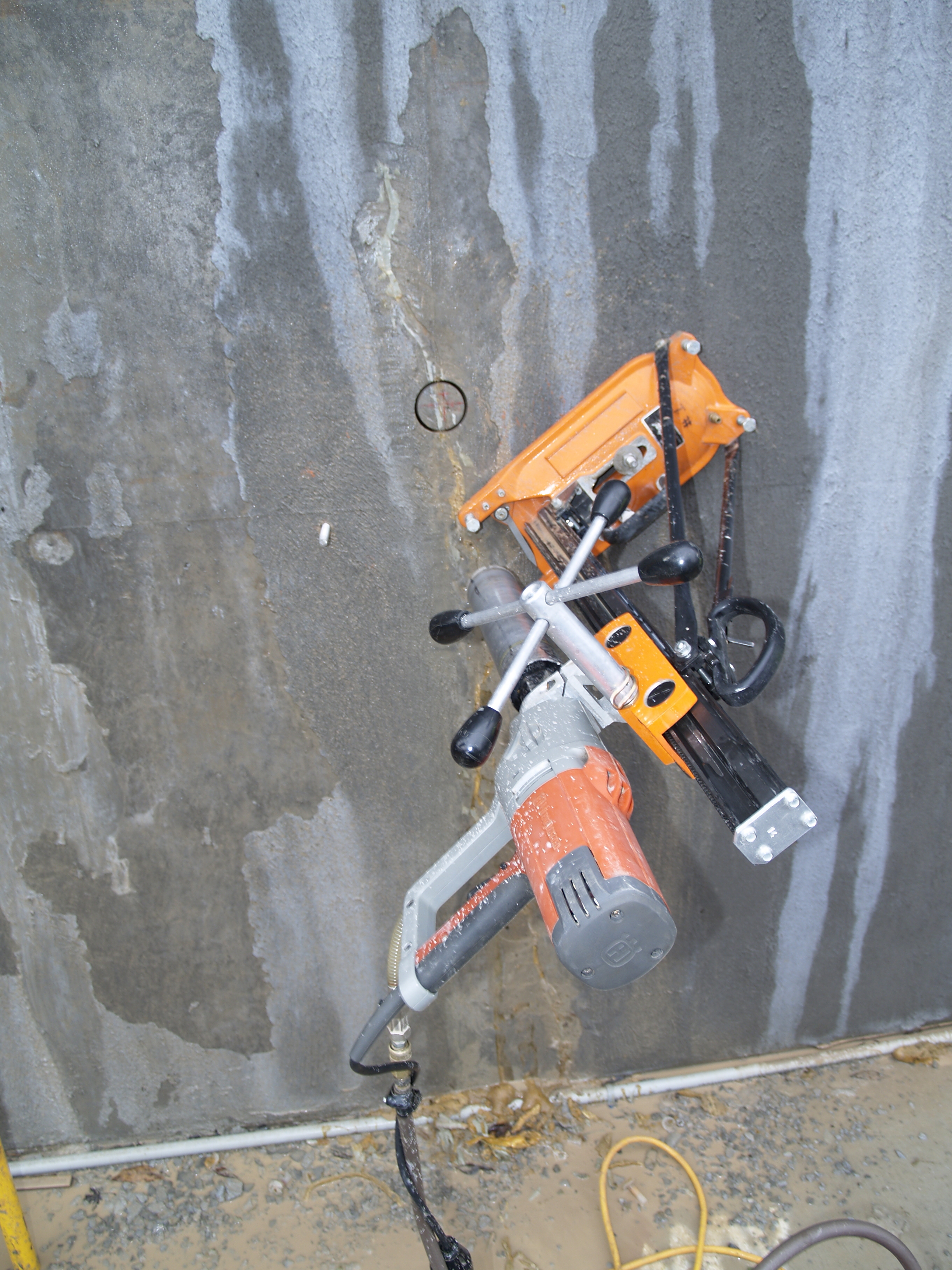
The objectives of the investigation were to determine the root cause of cracking in the dam structure, and to determine the anticipated service performance of the structure as influenced by this cracking. The investigation included laboratory studies, field investigations including flooding a portion of the structure to check for leaking, petrographic examination of concrete cores, and finite element analysis of the early-age thermal and mechanical behavior of the structure.
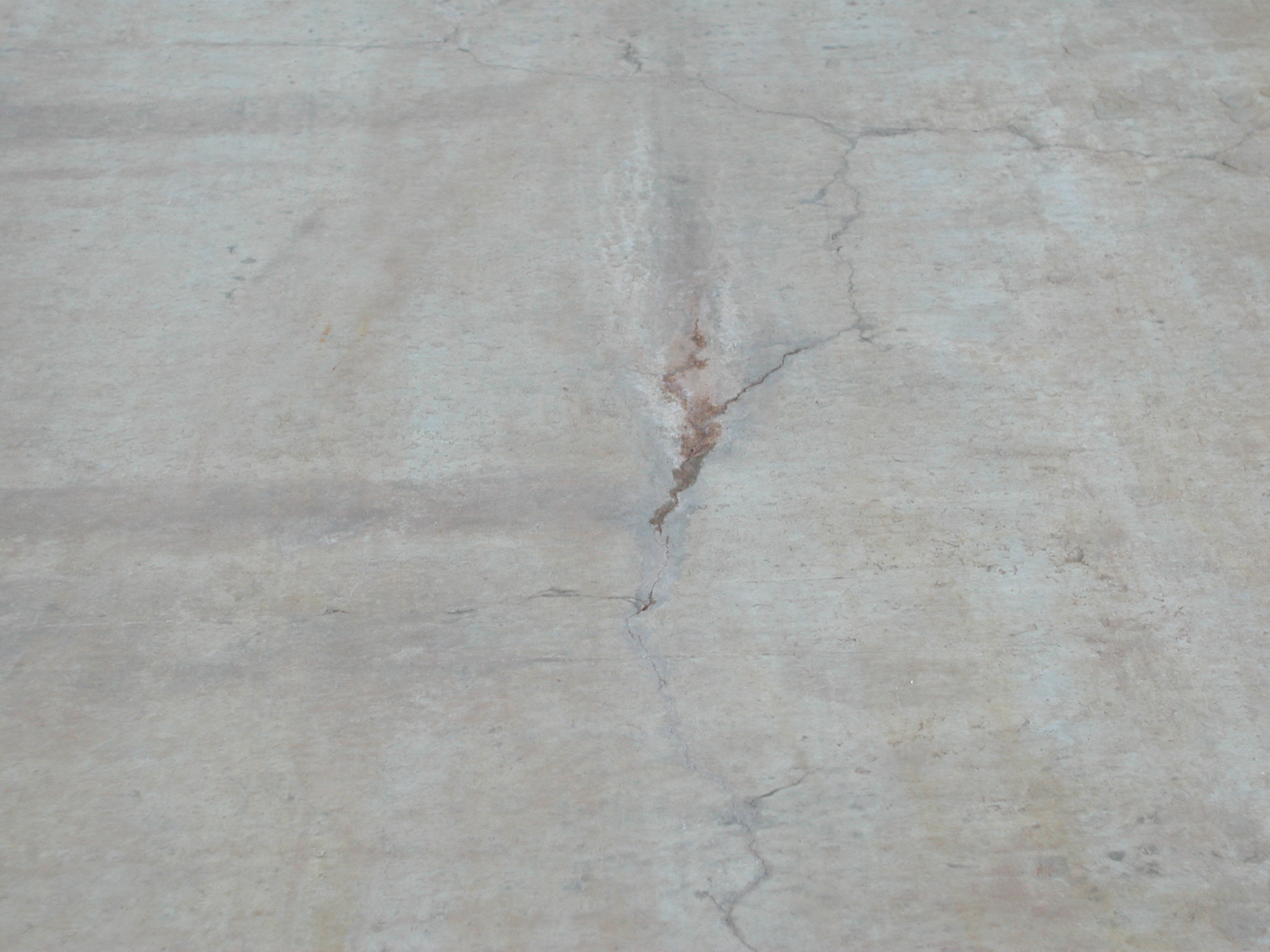
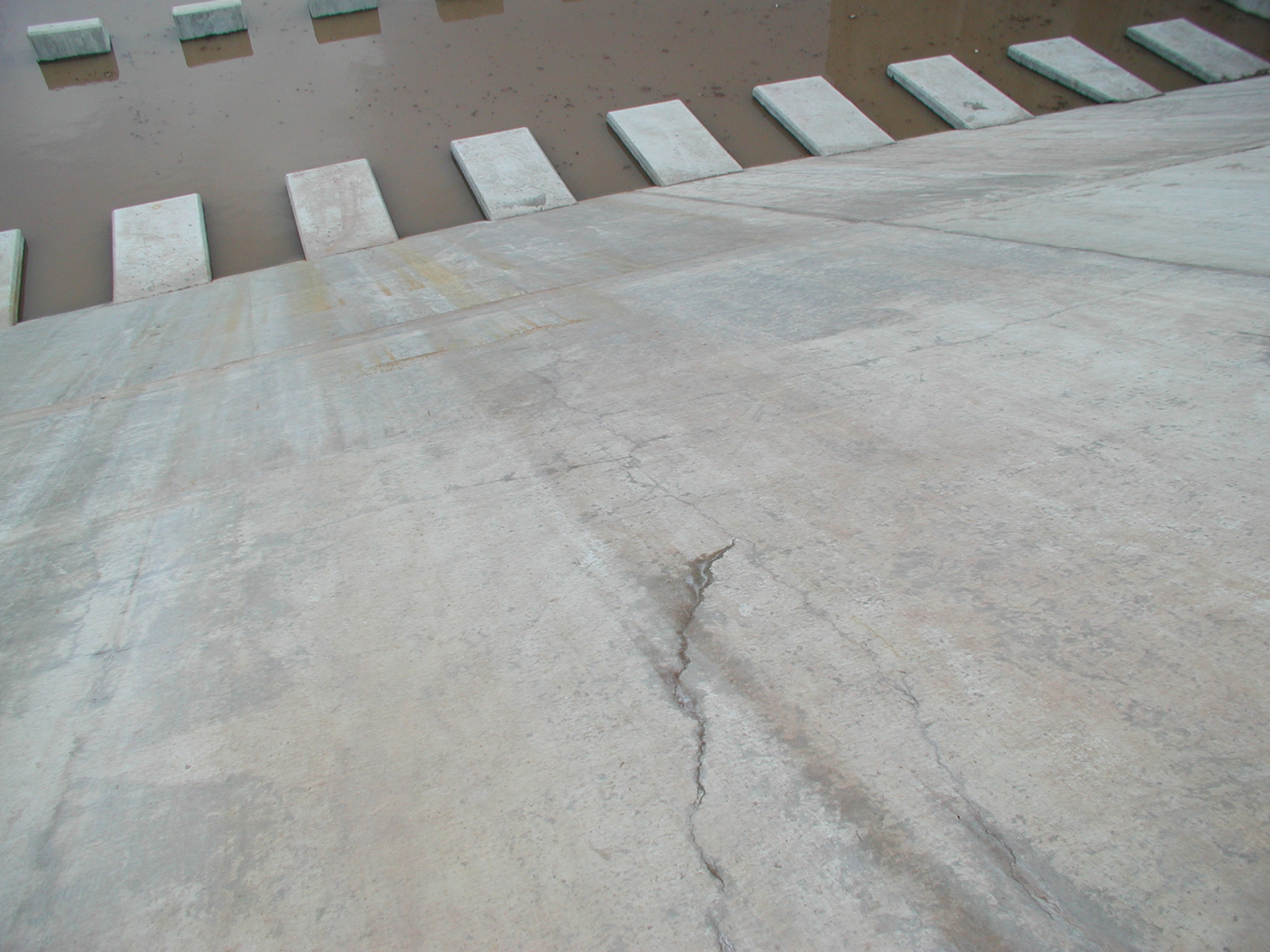
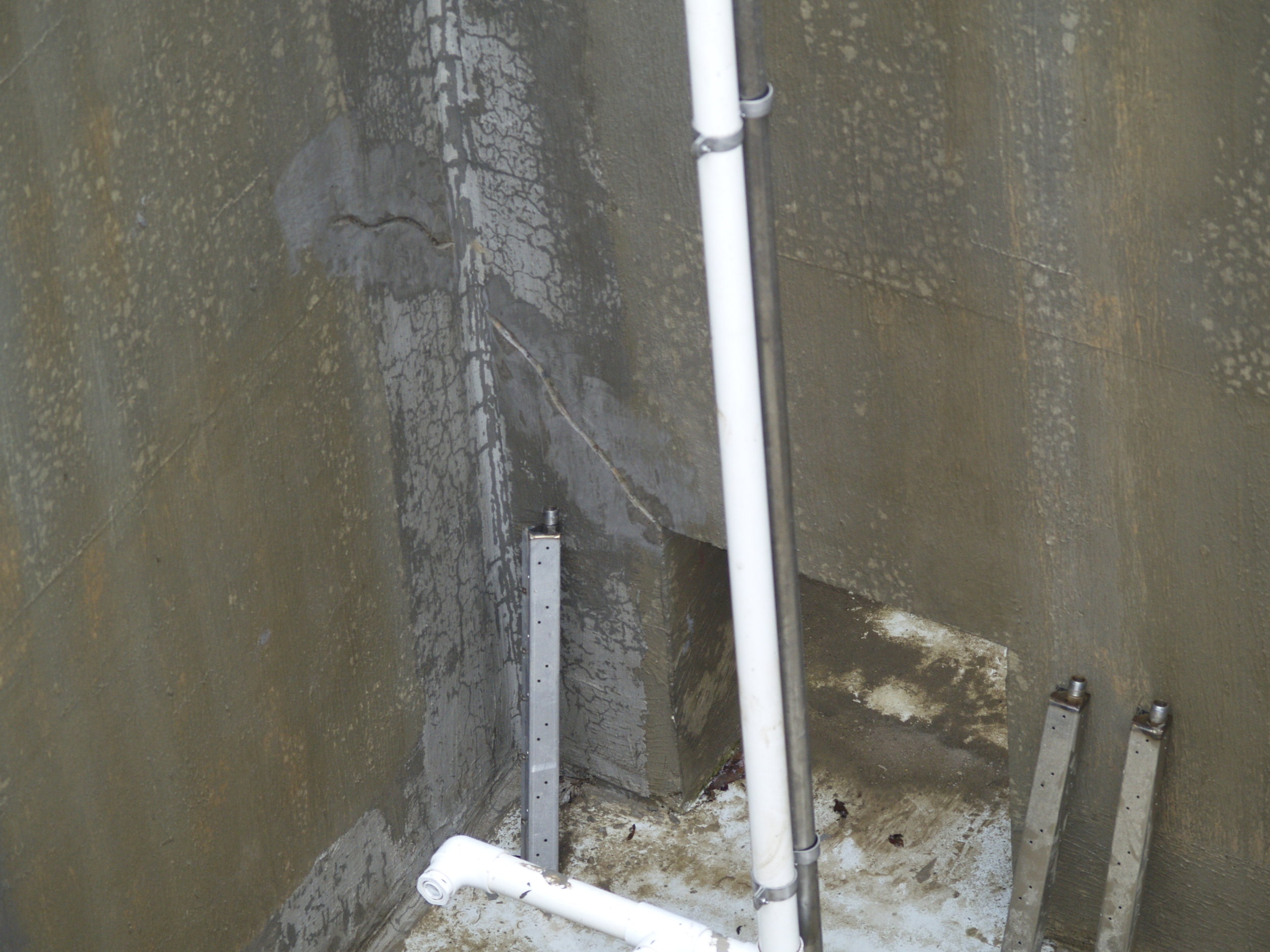
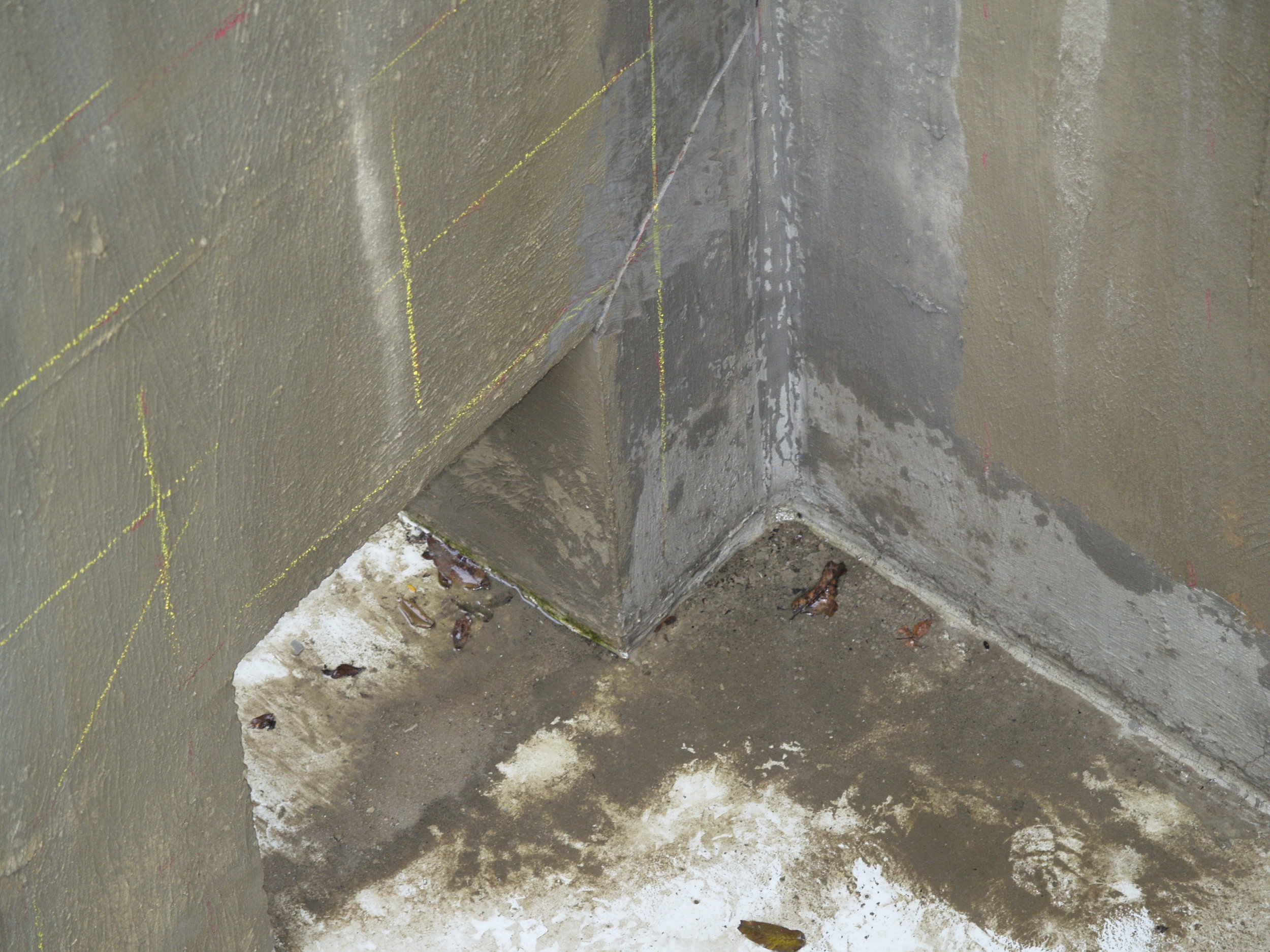
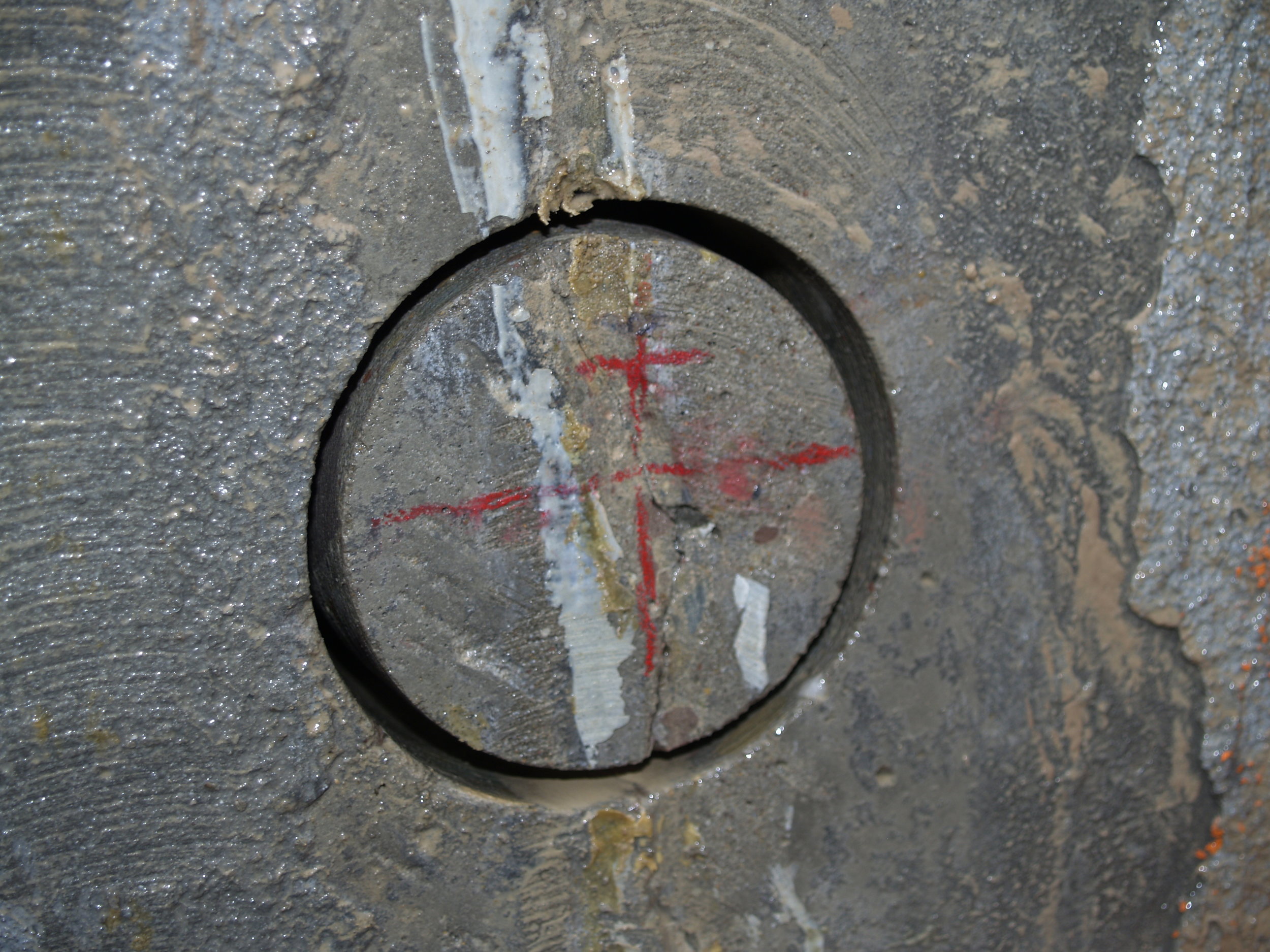
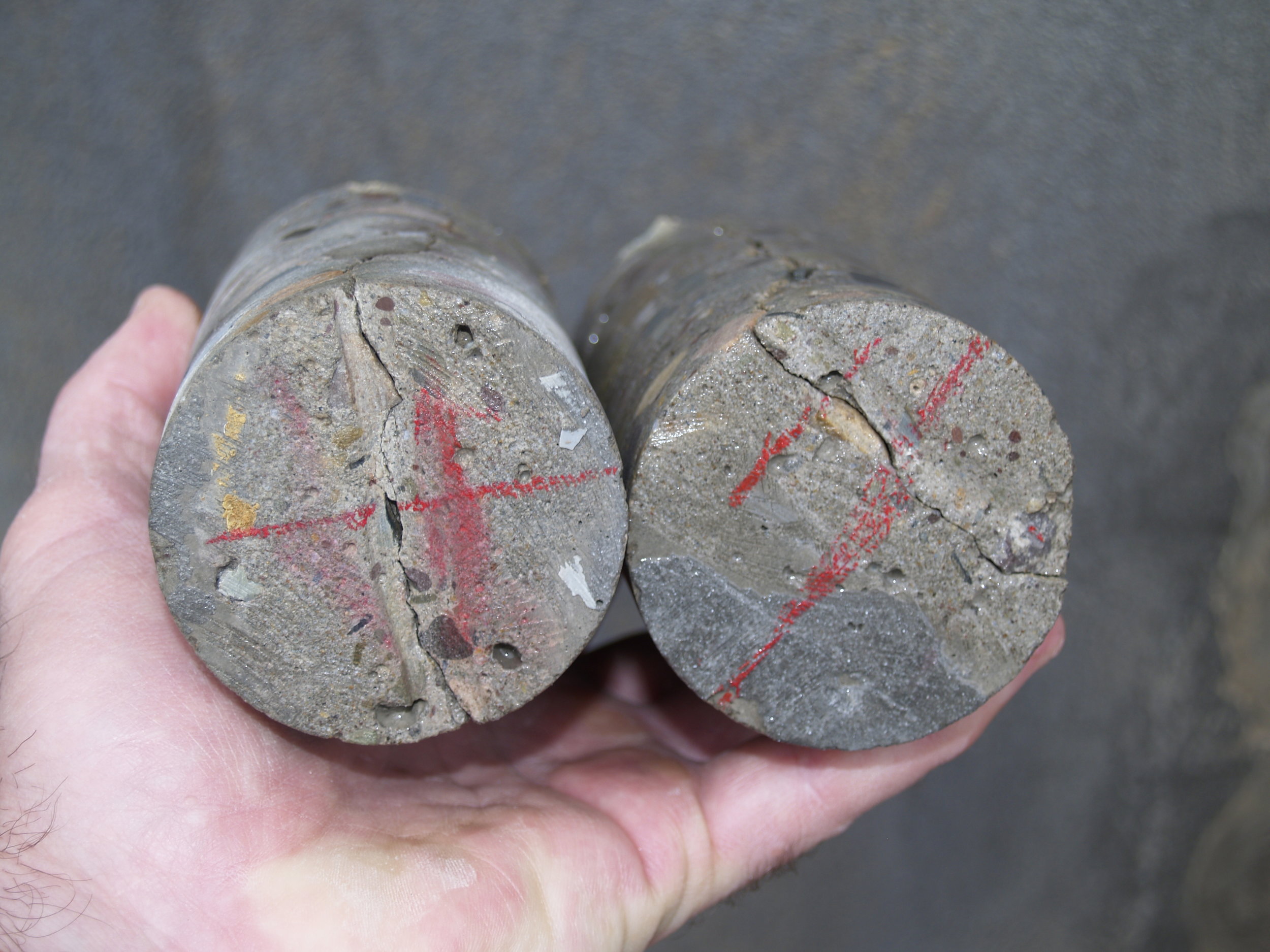
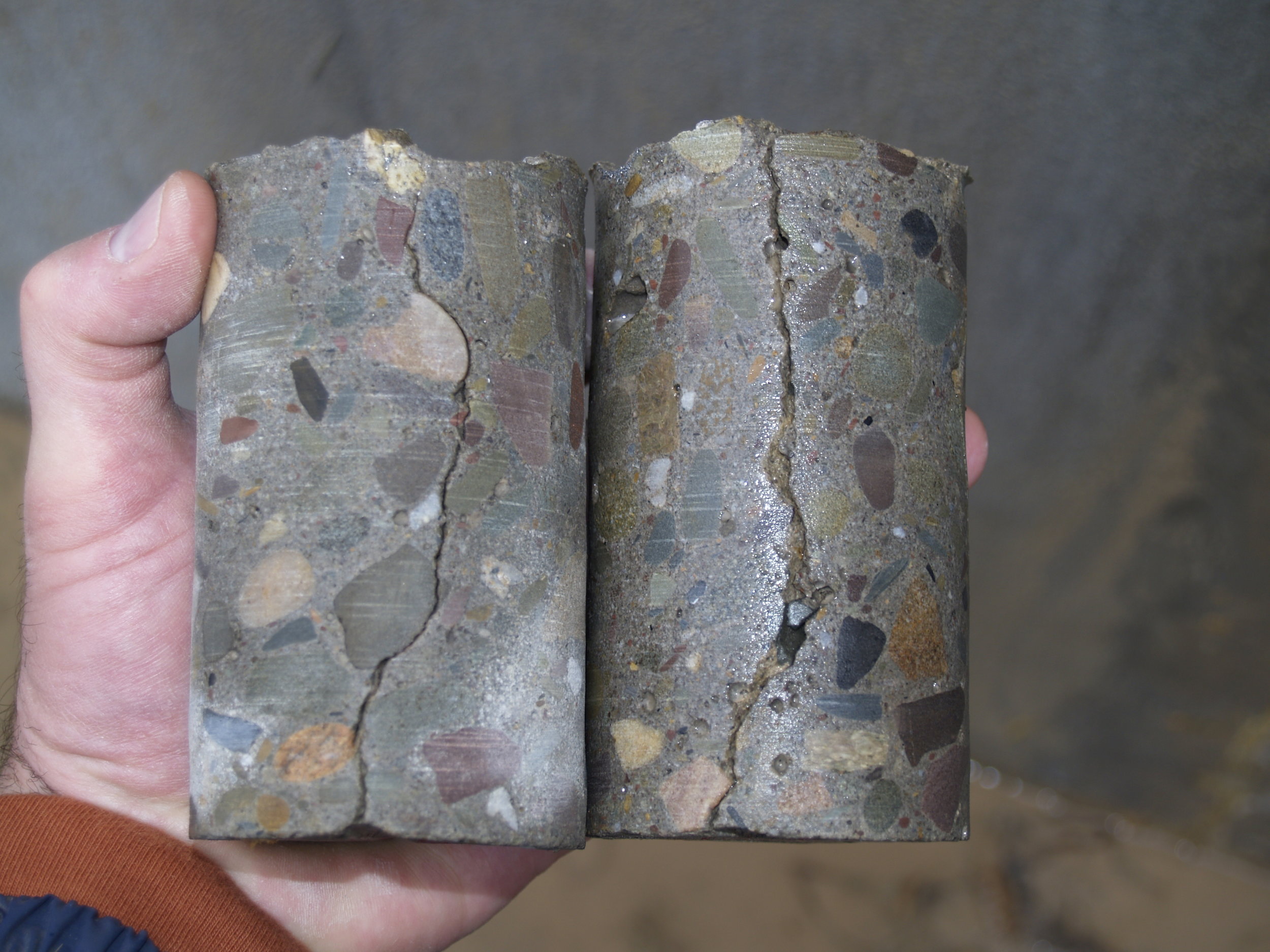
The root cause of cracking in the dam structure was determined to be caused by differential thermal expansion in the slabs early in the age of each slab. Peak tensile stresses in were predicted to occur through the thickness of the slab approximately 20 days from the date of concrete placement. Cores extracted from the structure showed that the cracks extend through the thicknesses of the slabs. Petrographic examination of the cores determined that the cracks have not undergone autogeneous healing, and that the cracks will not prevent water from leaking through the slabs. The petrographic examination did not find evidence of other possible causes of the observed cracking, namely improper curing, improper mixture proportions, or active deterioration mechanisms such as alkali silica reaction.
Several conclusions were drawn about the anticipated service performance of the dam structure. The dam structure would leak without repair. Water will enter the cracks on the upstream side of the structure and flow through the slabs to the roller compacted concrete below the slabs. Finally, recommendations were made for the repair of the structure. Those recommendations were implemented and the structure is now in service.
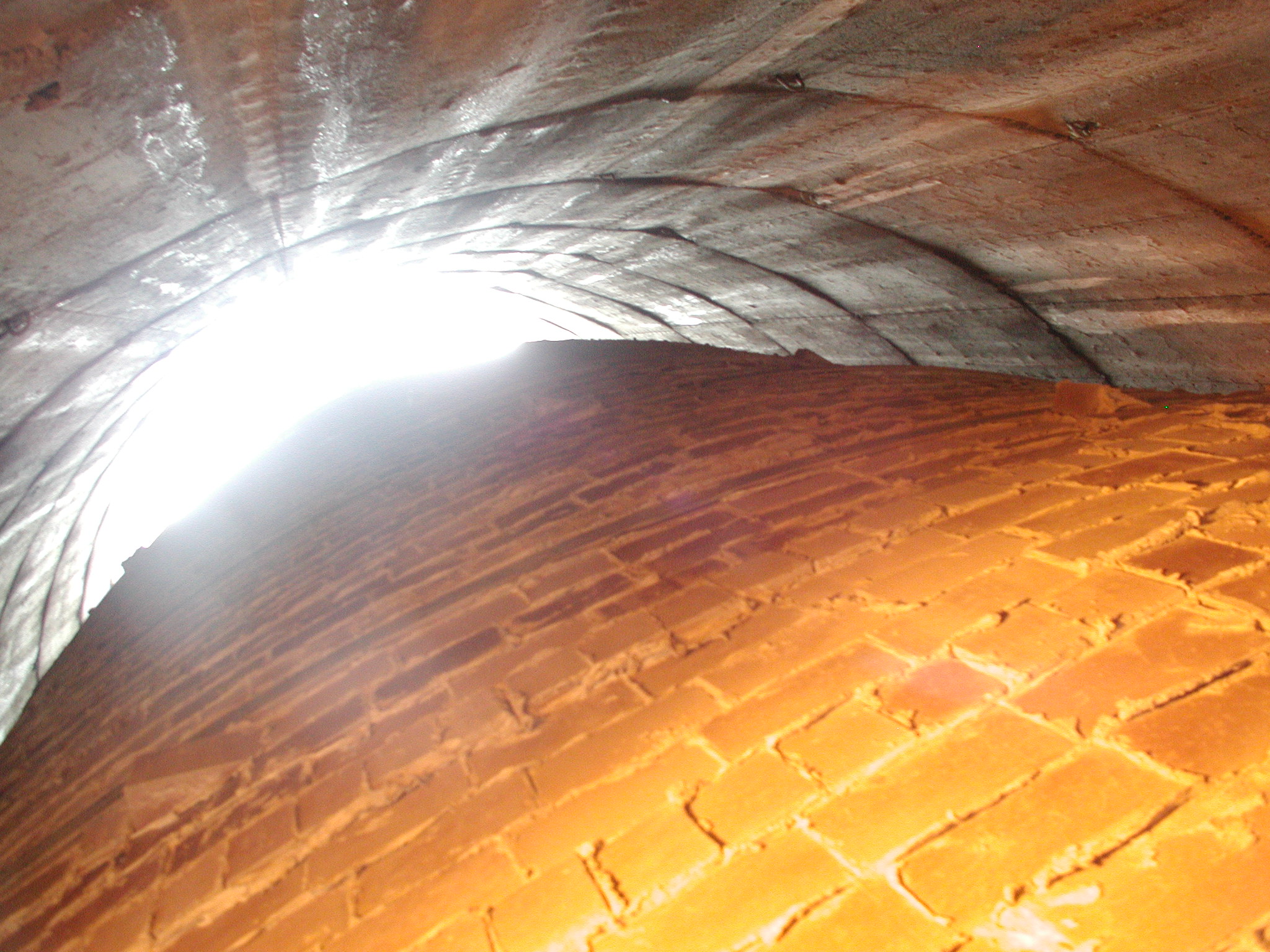
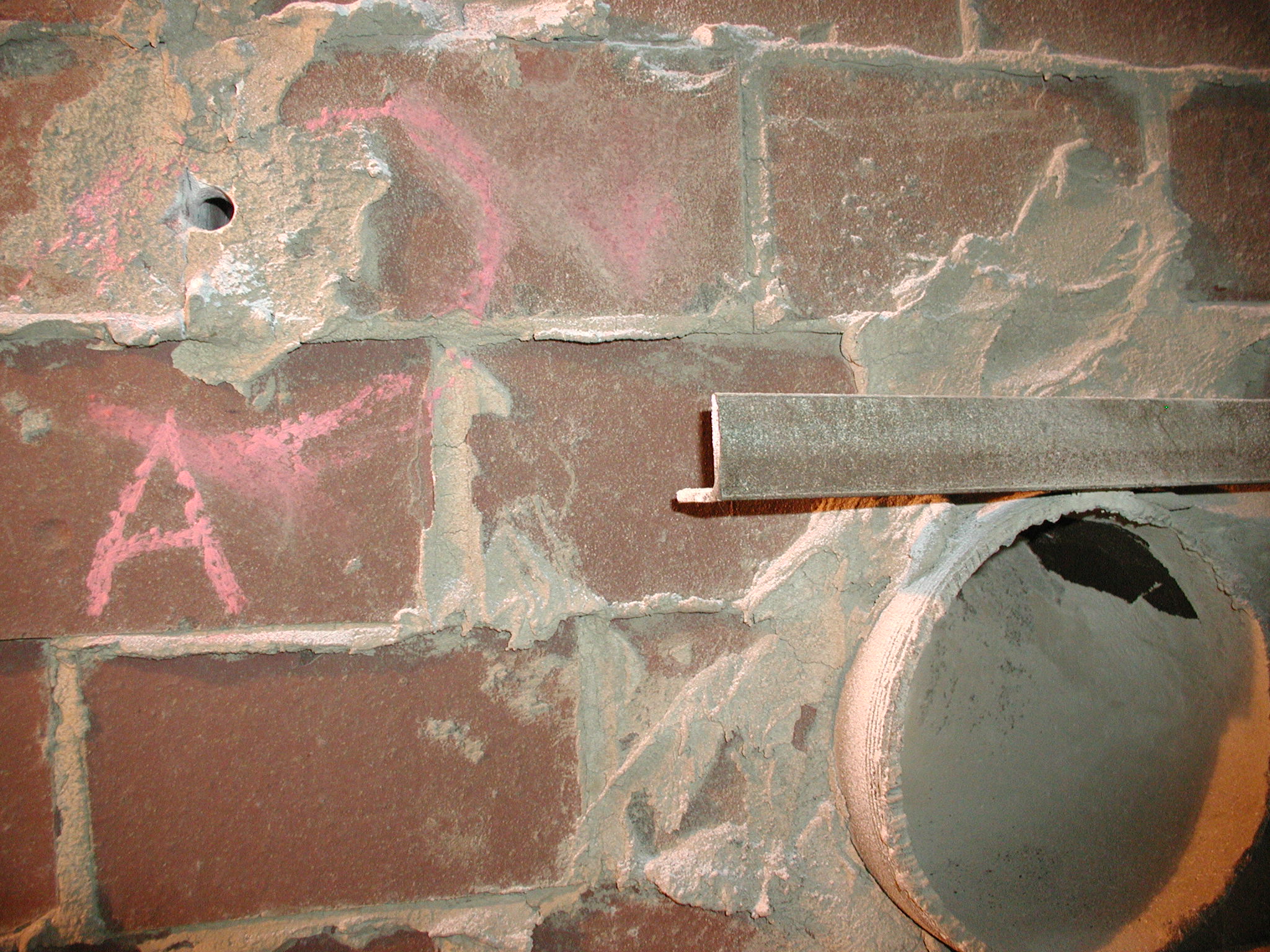
PROJECT: refractory brick chimney liner / CONDITION ASSESSMENT
SCOPE OF WORK: Forensic Investigation / Materials Evaluation
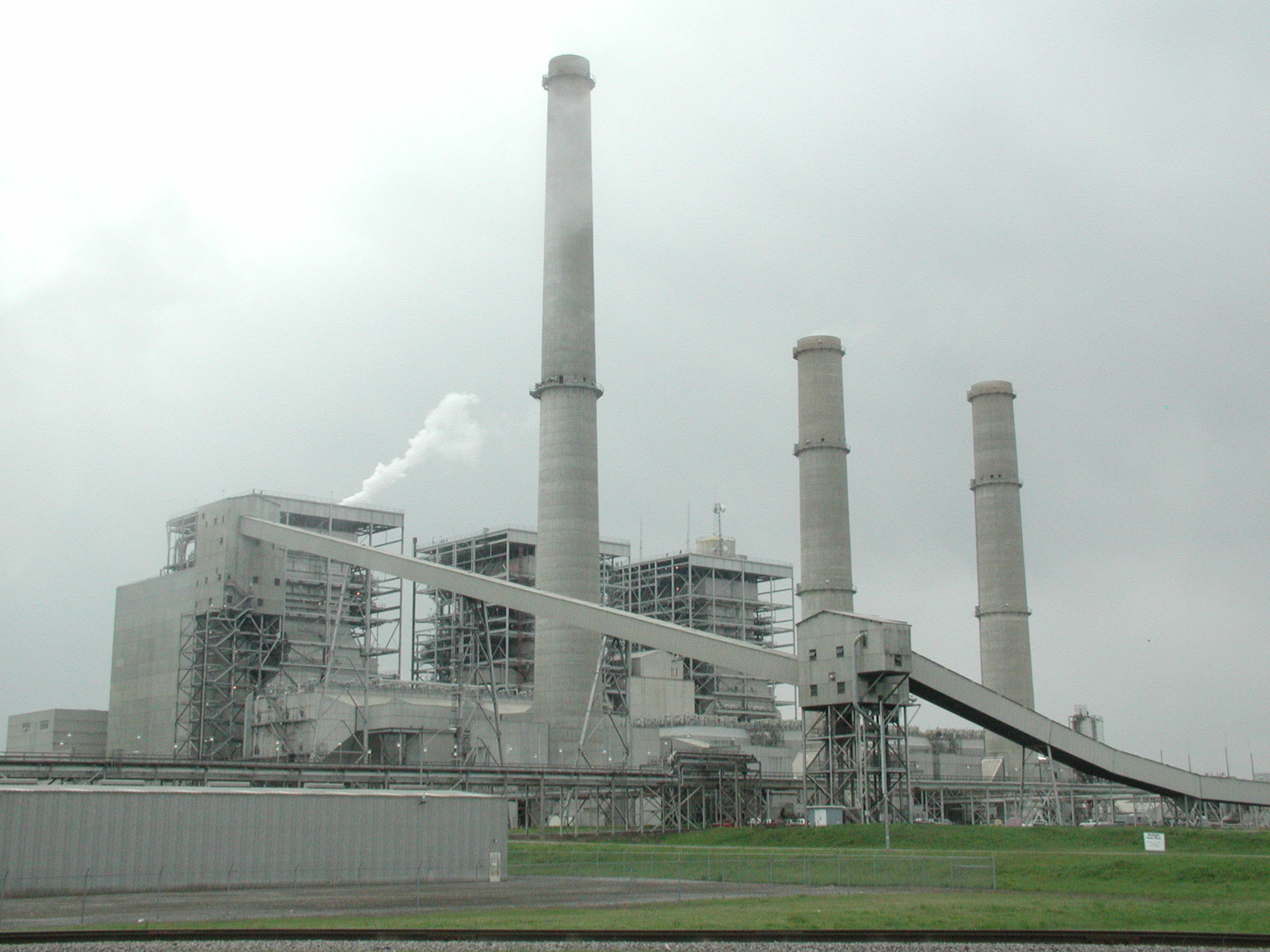
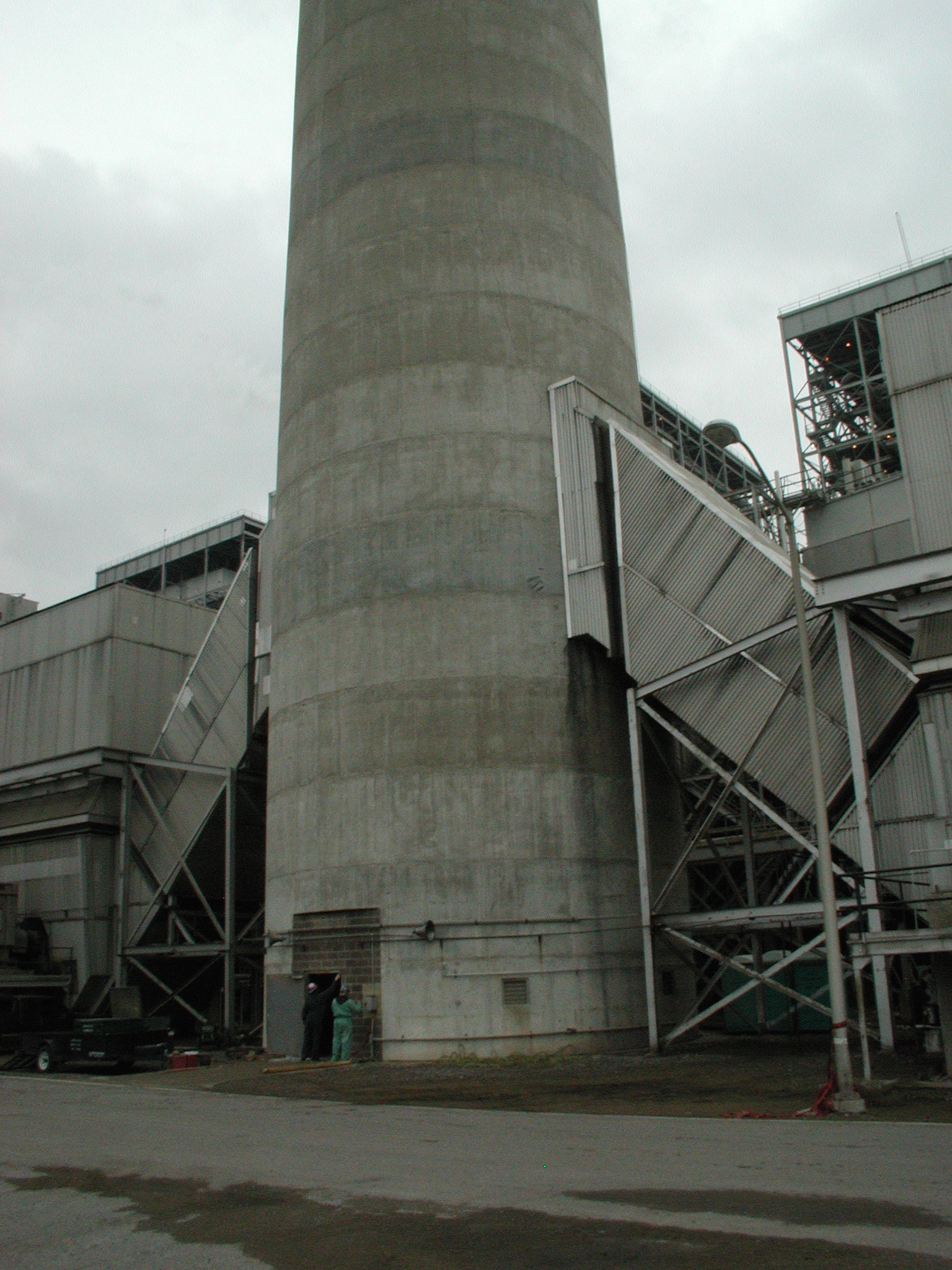
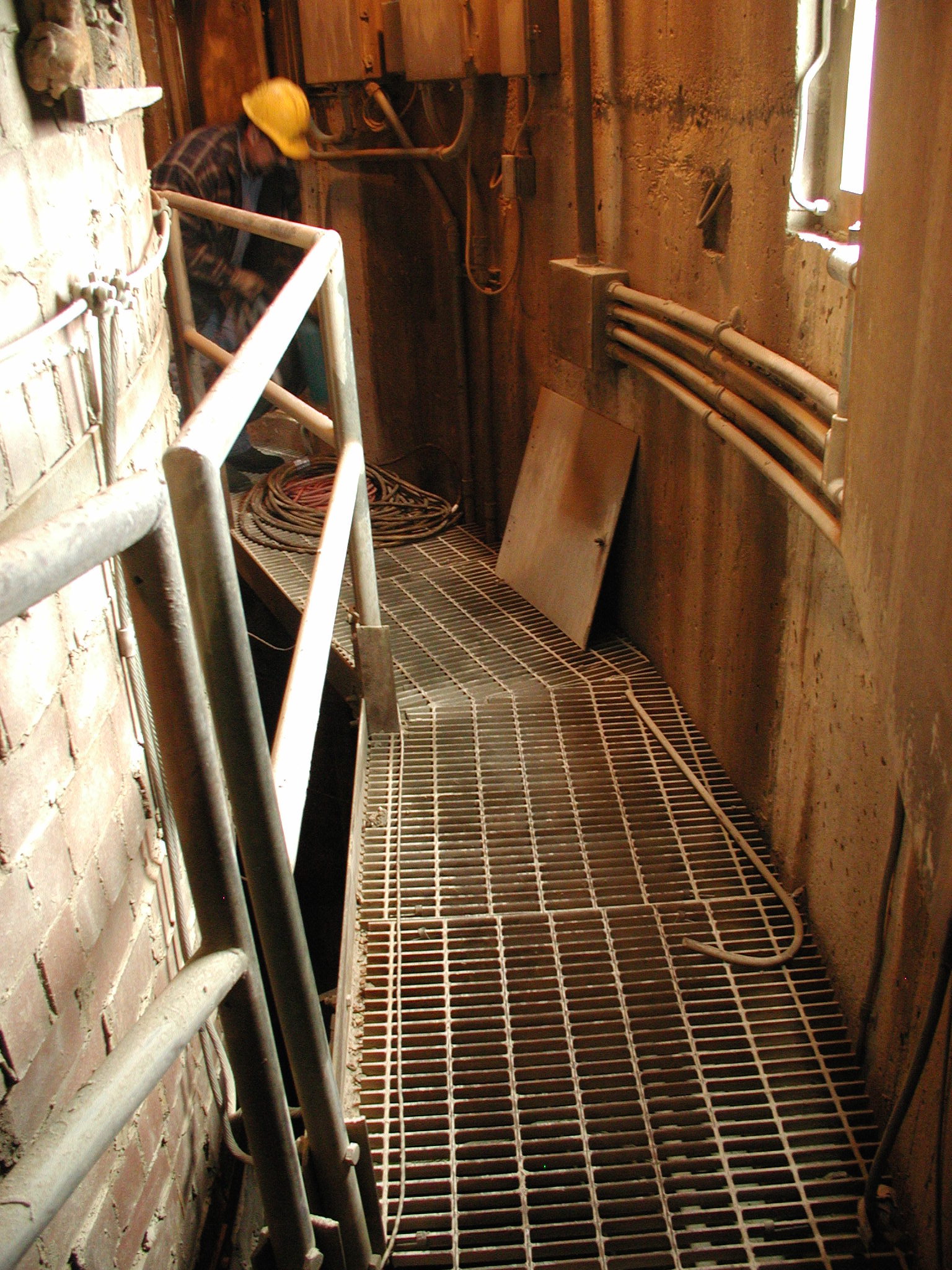
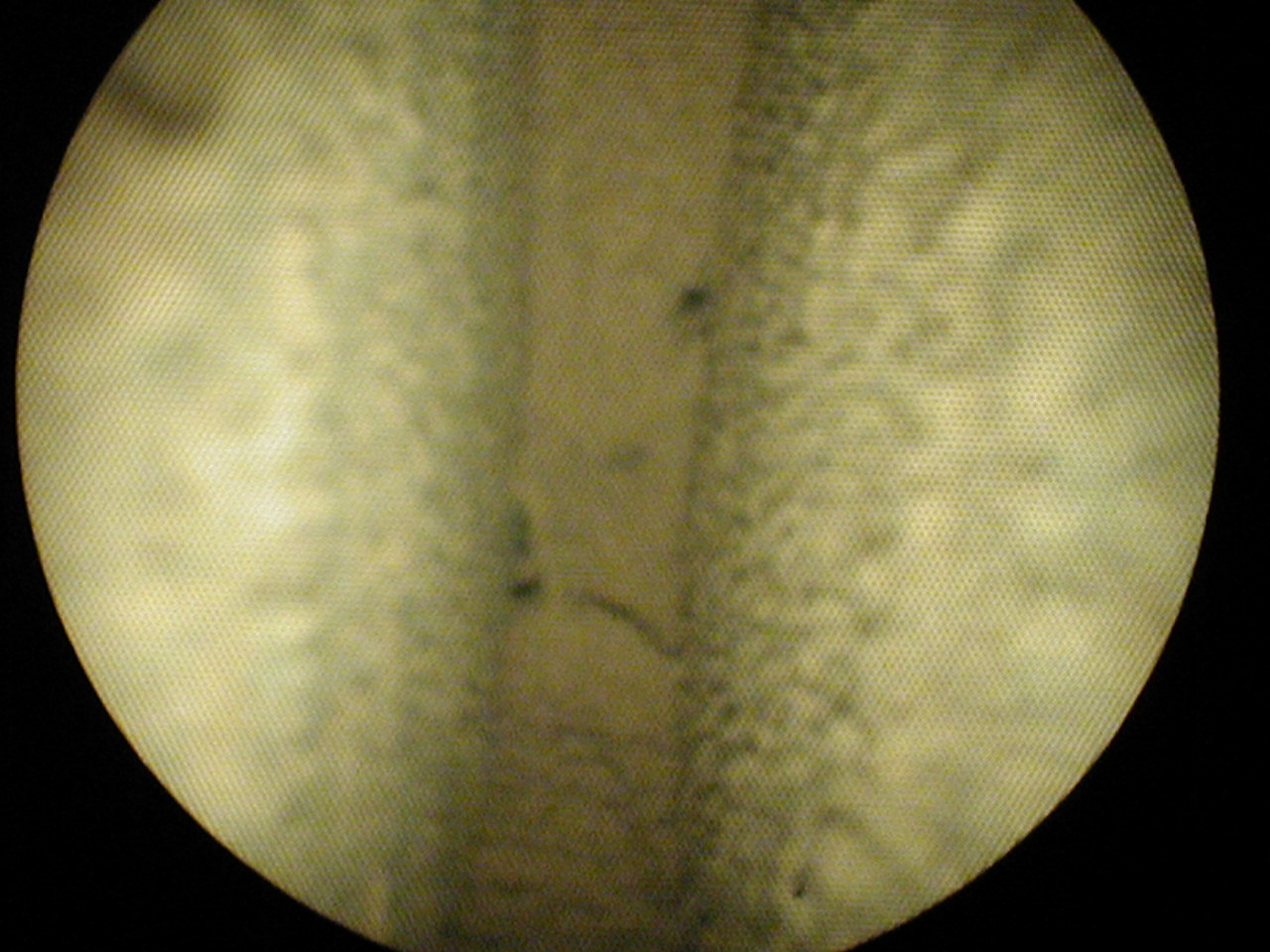
The objective of the investigation was to assess the condition of a refractory brick chimney liner in a coal-fired power plant that was off-line for maintenance. A visual inspection by the utility company revealed conditions that warranted a more detailed inspection of the liner. A borescope was used to probe several locations in the liner to visually inspect and document the interior condition the liner.
PROJECT: WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT / CRACKING and serviceability EVALUATION
SCOPE OF WORK: Forensic Investigation / Materials Evaluation
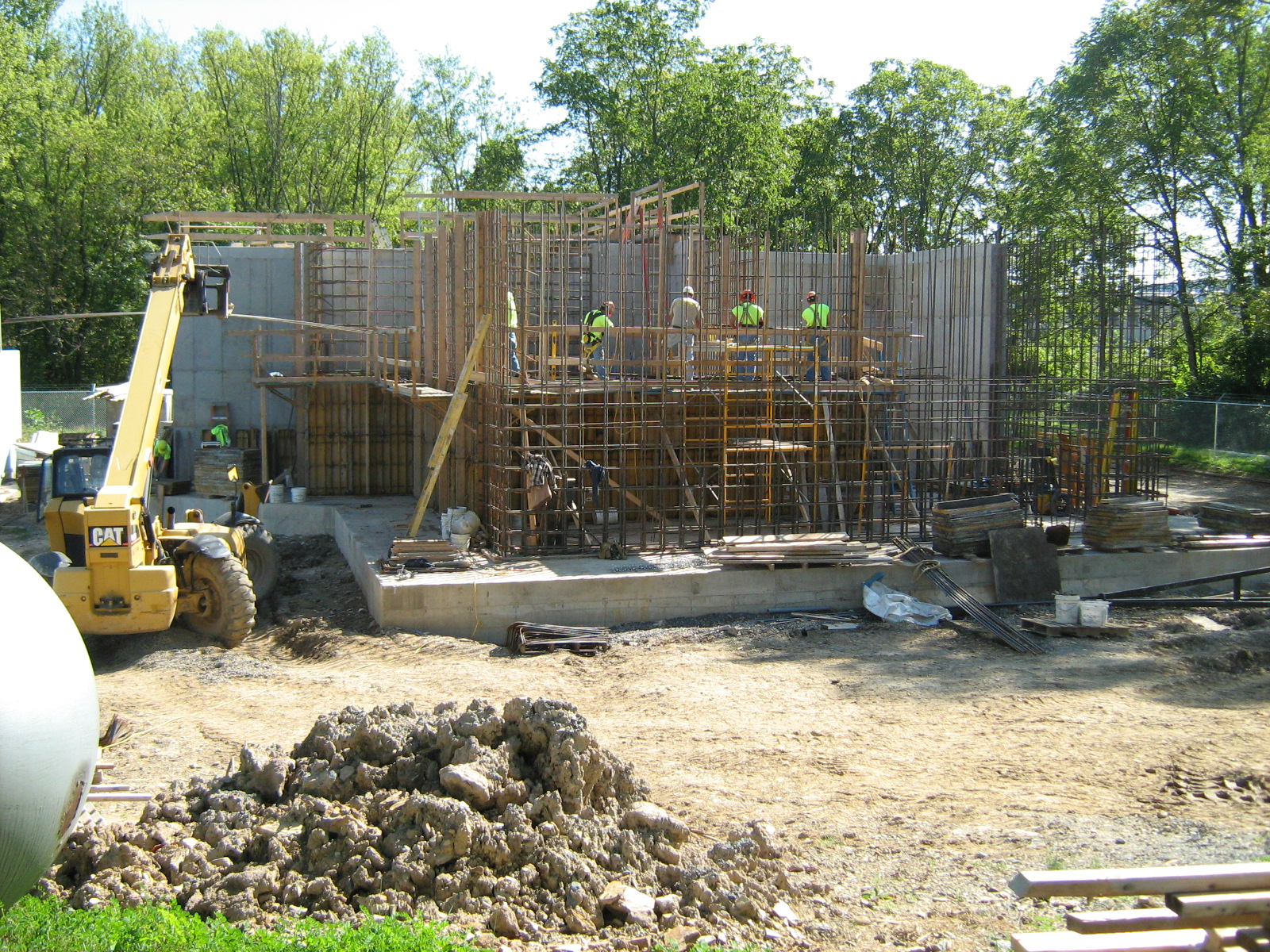
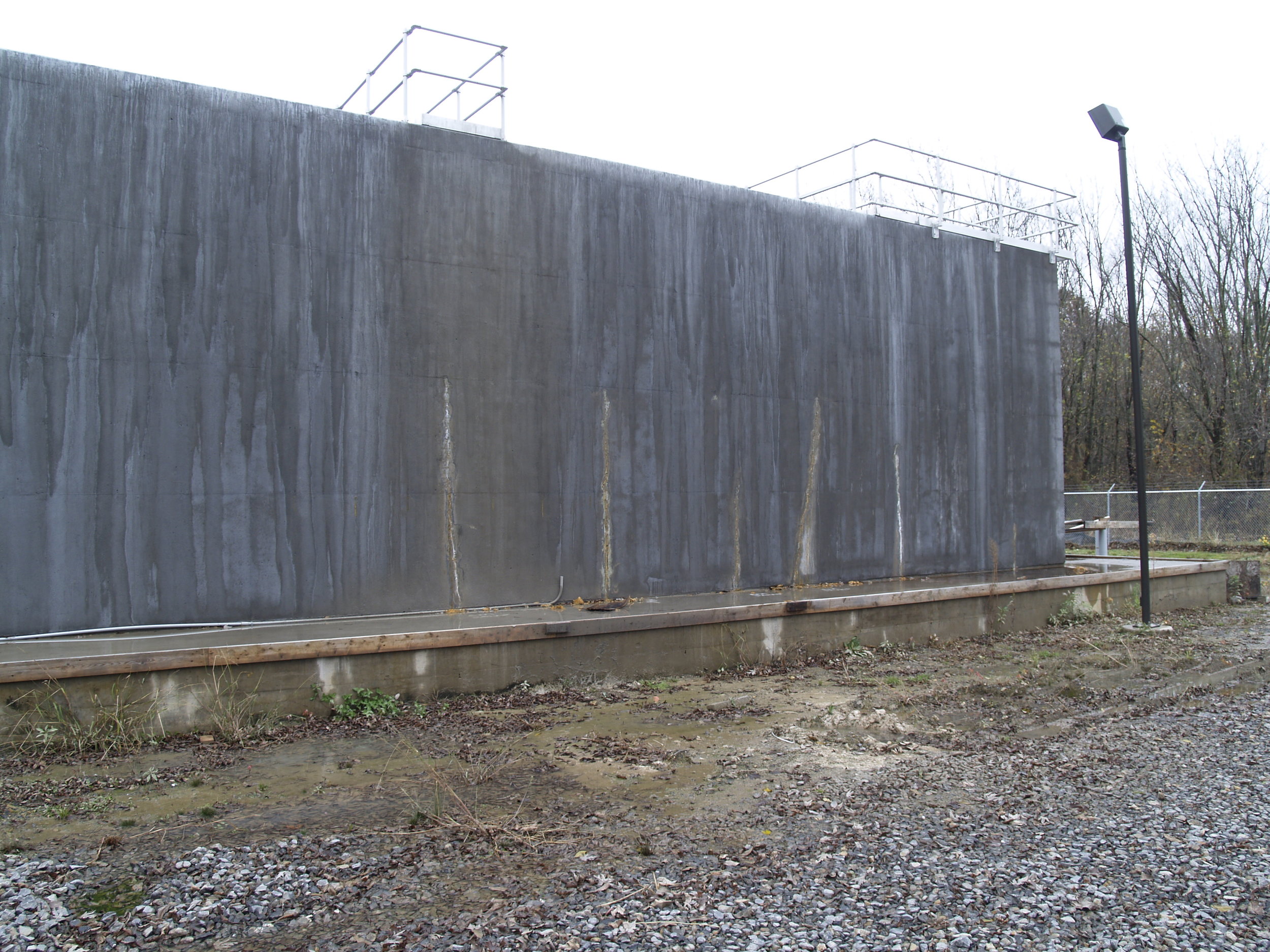
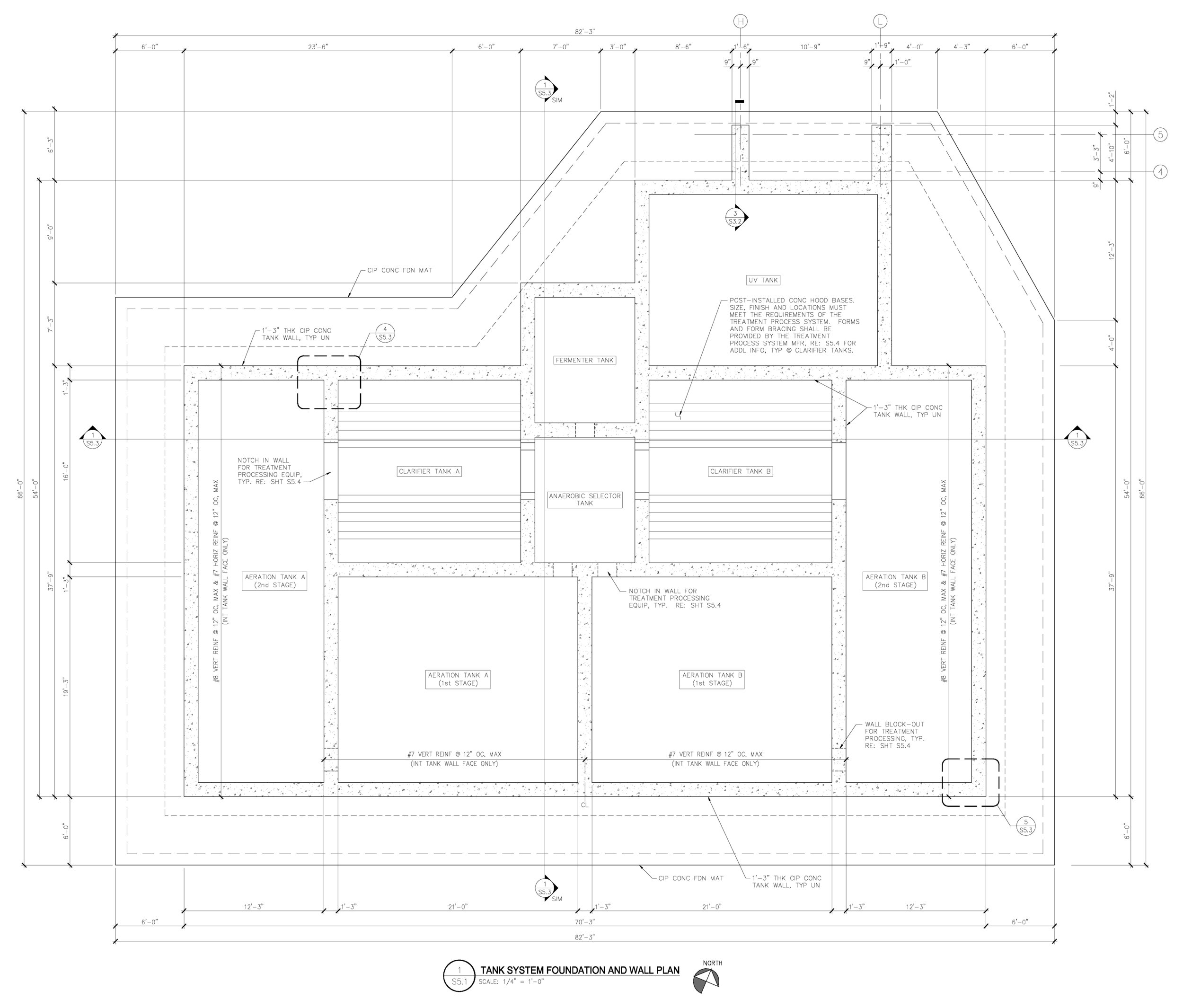
This project involved an investigation of concrete cracking in a newly constructed wastewater treatment plant in Snyder County, PA. The purpose of the investigation was to determine the cause(s) of the observed cracking, and to make recommendations for repair or replacement of the structure. The scope of work included a review of background information; site visits; core sampling for petrographic examination of the concrete; a review of the design calculations; and, recommendations for repair.
The structure is a cast-in-place reinforced concrete tank comprised of reinforced concrete walls on a reinforced concrete mat foundation. The overall plan dimension of the mat foundation is approximately 82’-3” x 66’-0”. The mat foundation is predominantly 2’-0” thick, and increases to approximately 5’-4” thick along the perimeter haunch. The plan configuration of the mat roughly follows the plan configuration of the walls. The reinforced concrete walls are 1’-3” thick and 17’-0” high and do not include expansion joints.
During construction, the formwork for the walls was removed as soon as possible after the concrete was placed, and that would typically mean that the formwork was removed a day or two after concrete placement, or if the placement was towards the end of the week, the formwork would be removed early the following week. Once the formwork was removed, no measures were taken to wet-cure the walls, and no curing compounds were applied to the walls.
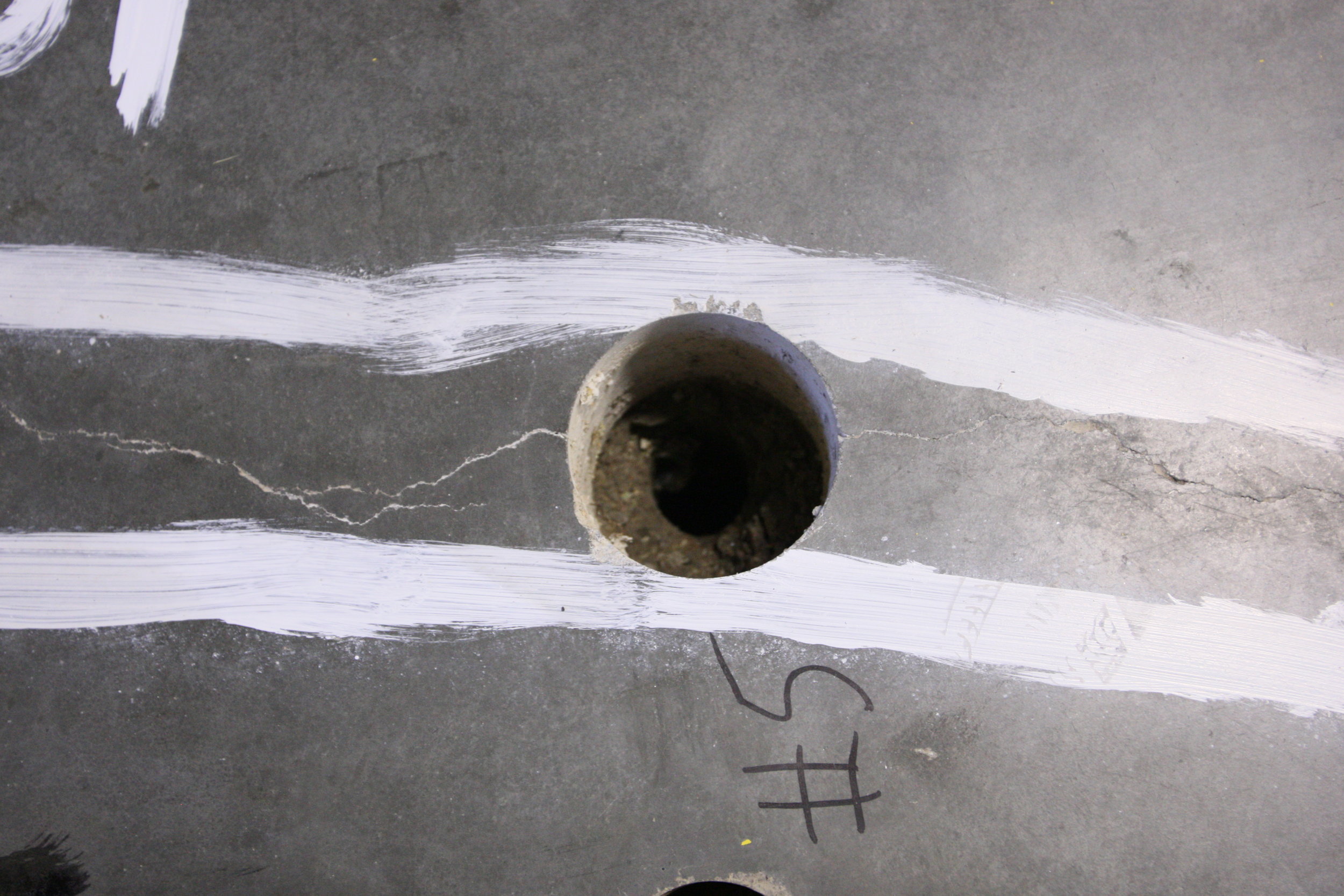
Two distinct configurations of cracks were observed in the walls of the structure. Most of the observed cracks were aligned more or less vertically along the walls of the structure. These crack were caused by restrained concrete shrinkage (restraint at the base of the walls by the mat foundation). One particular inclined crack was attributed to the combined effects of restrained concrete shrinkage and a stress concentration caused by a wall opening between the first and second stages of an aeration tank when subjected to fluid loading. Inclination of the crack through the wall thickness was indicative of a shear mechanism. Importantly, this inclined crack was reported to increase in length during an early fluid loading test of the structure.
Recommendations for repair focused on leak prevention and a strength retrofit of the inclined crack.
project: BEAM-COLUMN CONNECTIONS IN A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME STRUCTURE / FAILURE ANALYSIS
SCOPE OF WORK: Forensic Investigation / Failure Analysis / Litigation Support
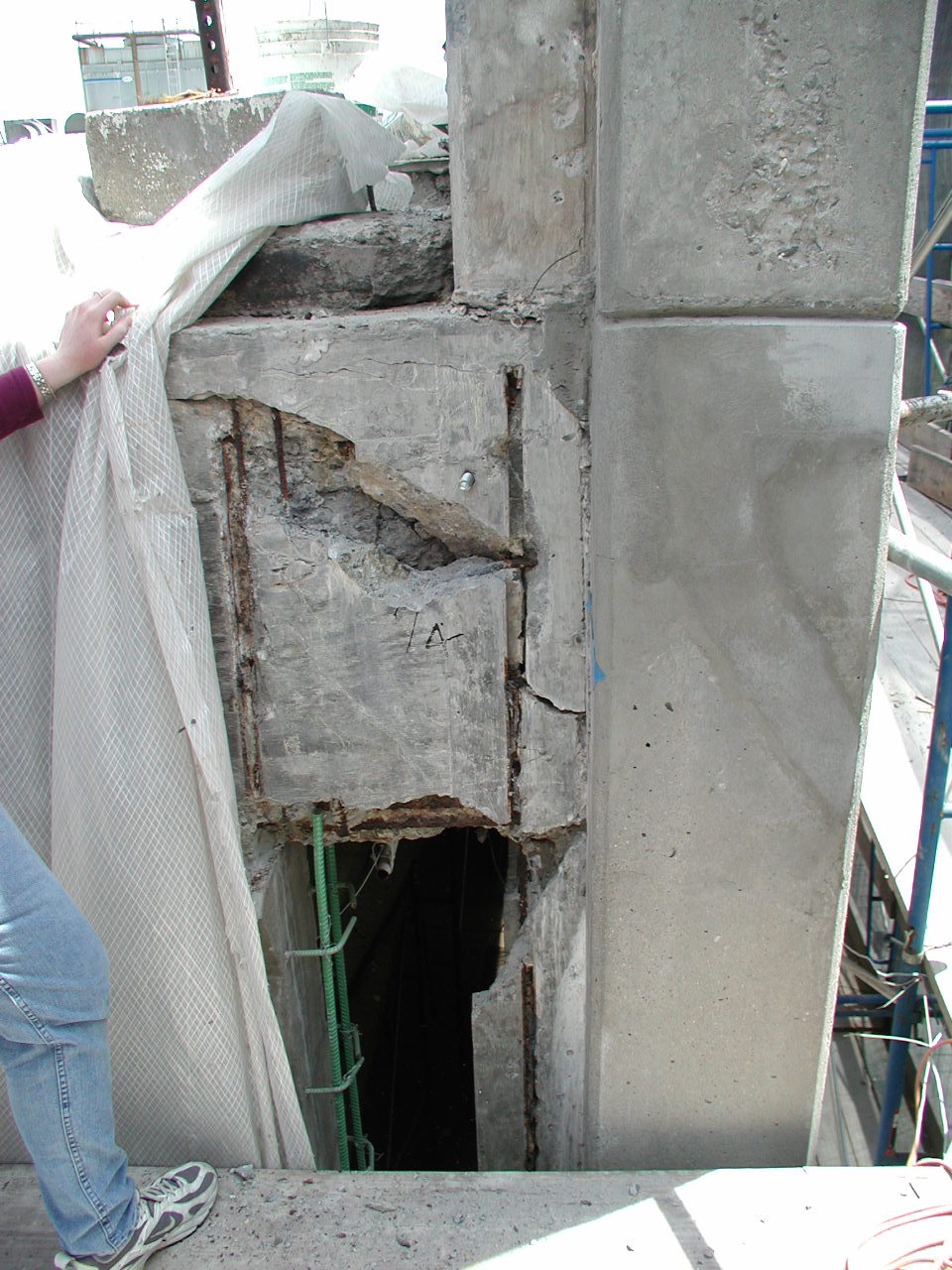
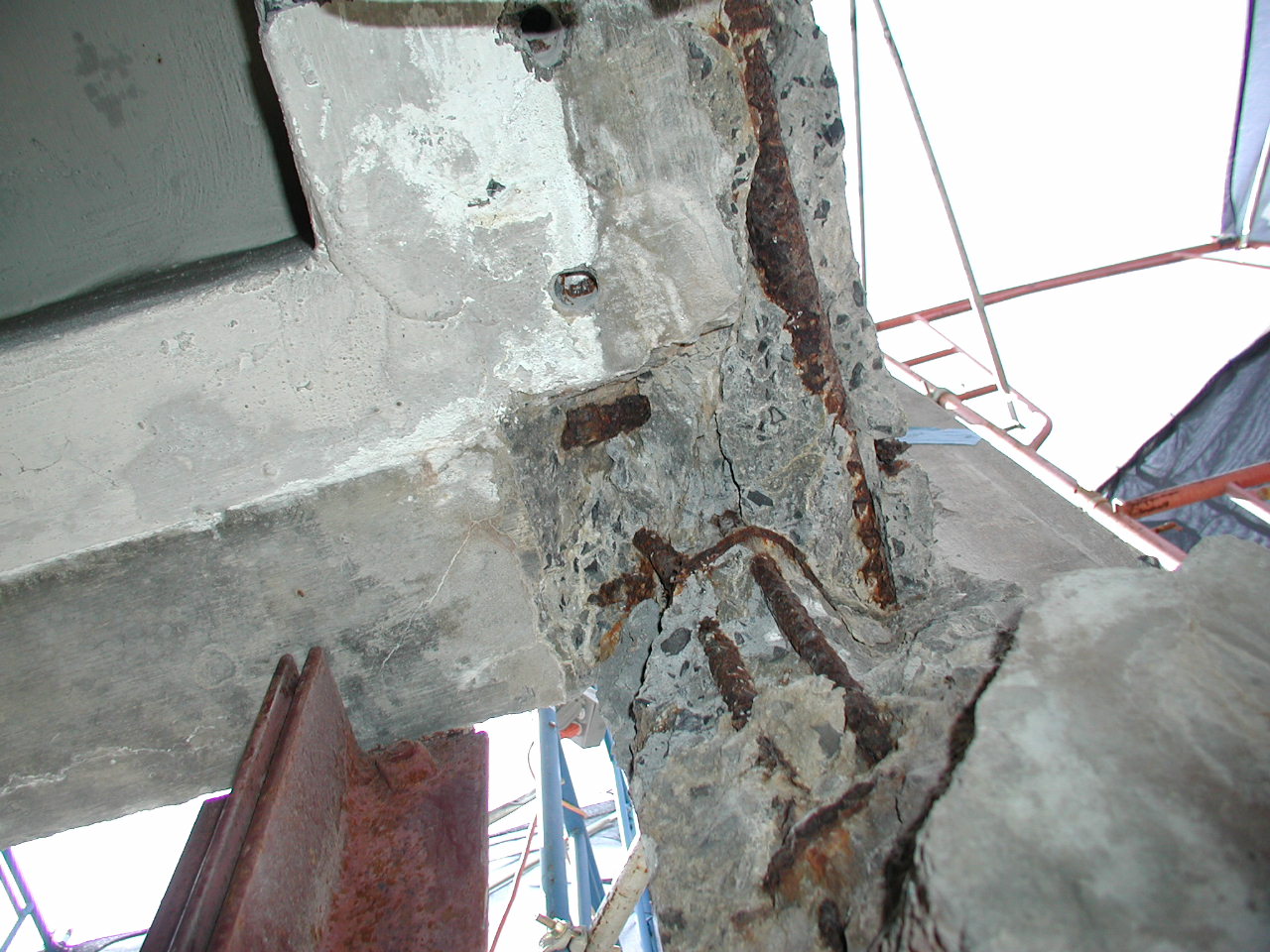
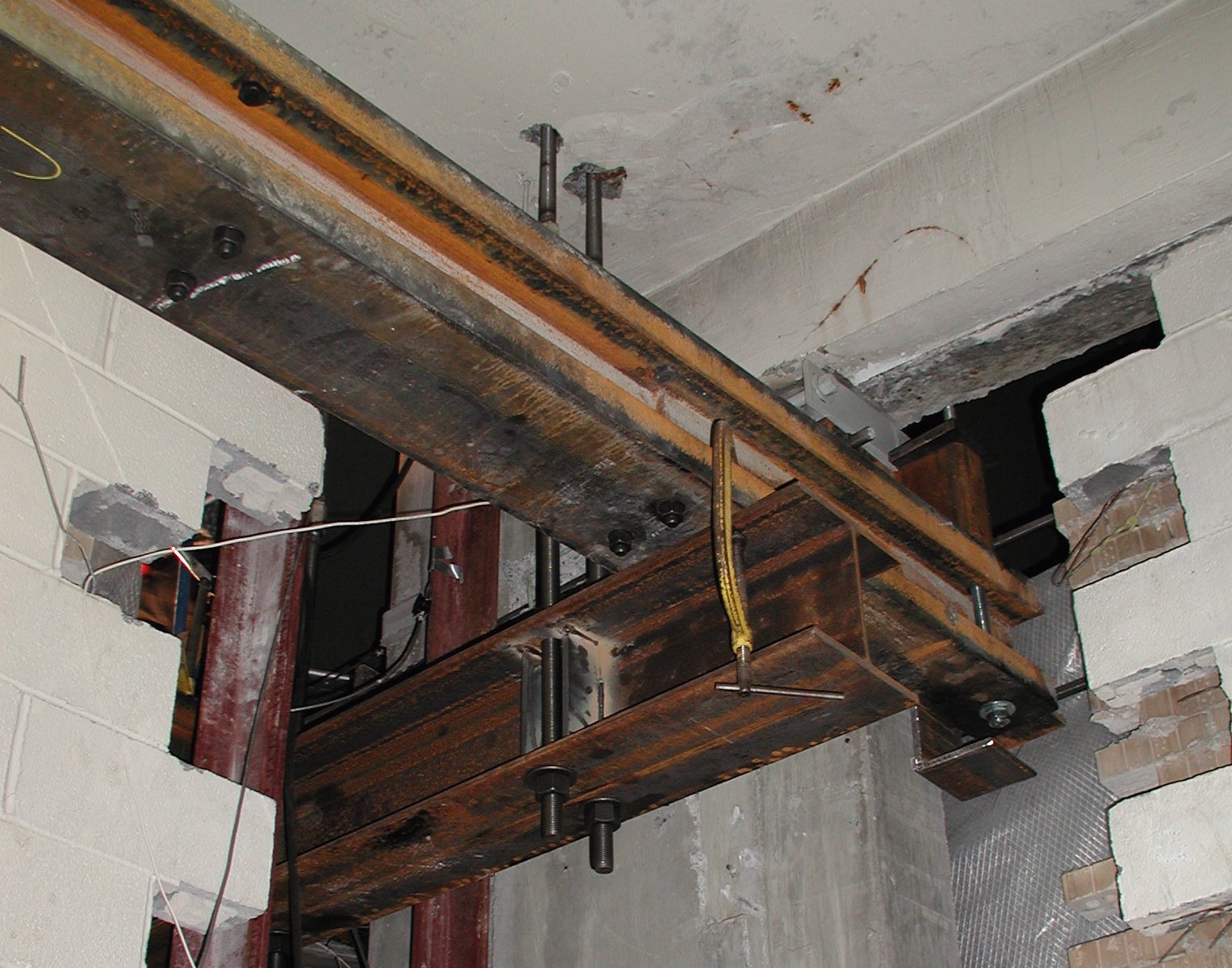
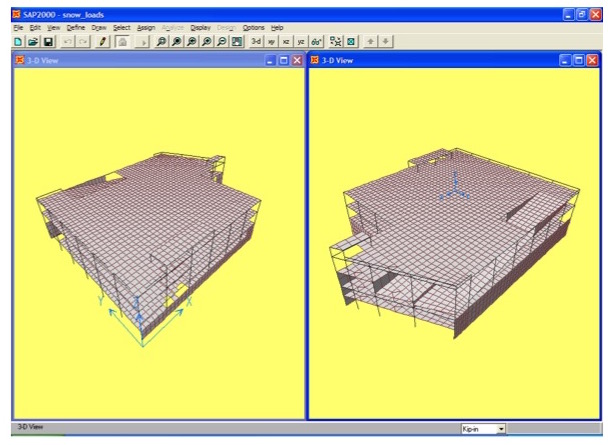
This project investigated the cause of structural damage in a low-rise reinforced concrete frame structure located in Long Island City, New York. Reinforced concrete elements that comprise the structure include walls, columns, posts, beams, waffle slabs, and solid slabs. The roof deck of the building is used for parking, accessed via a ramp at the north end of the structure. The structure included an exposed reinforced concrete frame with infill brick walls in the frame openings.
A series of structural analyses were performed to calculate the internal forces generated in the frame structure due to roof snow loads and brick expansion. The internal forces were then compared with member strengths to determine the consequences of the snow loads and brick expansion.
The snow loads used in the frame analyses were based on the 12-14 March 1993 snowstorm that struck the eastern seaboard of the U.S. Snow depth and water equivalent data were available from measurements taken at LaGuardia Airport. Included in the analyses of snow load was the effect of plowing the snow on the roof to accommodate parking, the consequence of which was to concentrate the weight of the snow in selected regions of the roof deck at which structural damage was observed. The brick expansion values used in the finite element analyses were based on measured values from material tests, as well as industry-recommended values from the Brick Institute of America.
The study concluded that the damage to the reinforced concrete frame structure is consistent with the damage that would be caused by an overload placed on the roof parking deck. The damage was exacerbated by the lack of repair of the structure and the fact that the structural frame was exposed to the weather as part of the architectural design of the structure. Further, it was determined that the damage was inconsistent with the damage that would be caused by brick expansion.
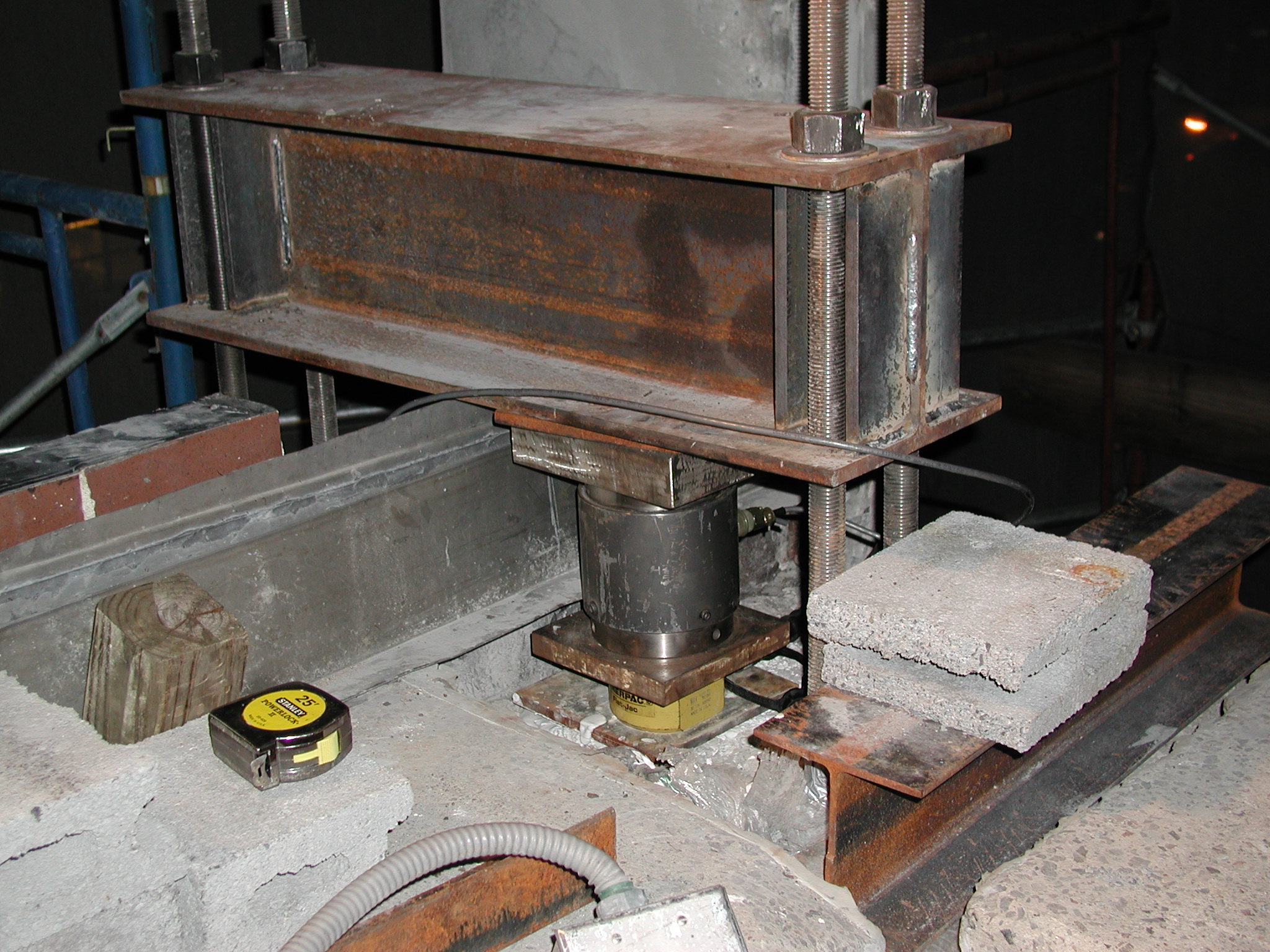
Finally, a load test was performed on one repaired beam-column connection at the roof level.
PROJECT: INDUSTRIAL FLOOR SLAB WITH RADIANT HEAT TUBING / cracking and serviceability evaluation
SCOPE OF WORK: Materials Evaluation / Litigation Support
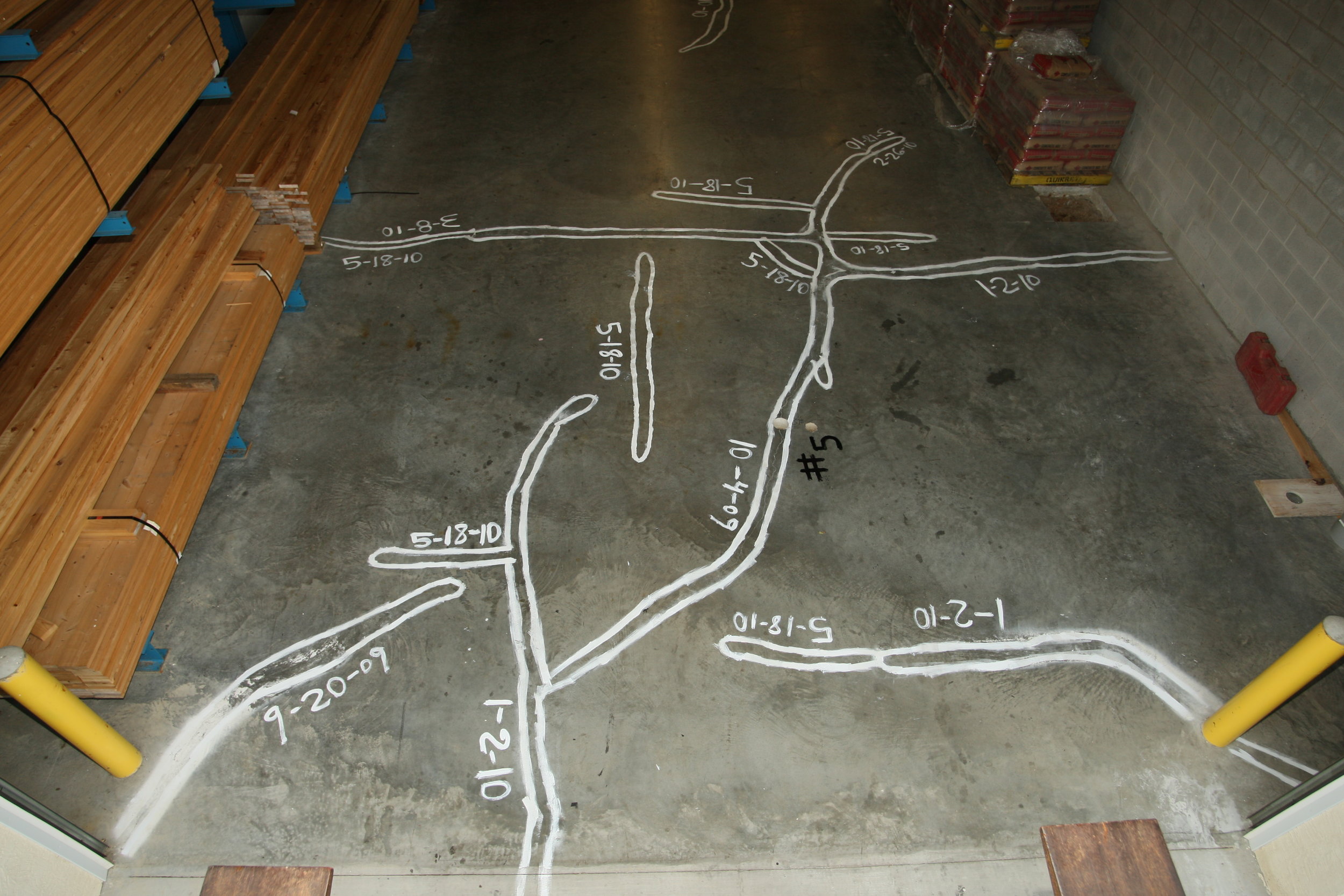
This project investigated the cause and long term performance consequences of cracking in an industrial concrete floor slab. The cracking appeared during construction, and continued to develop as the structure was put in to service. Several opinions were offered by experts to explain the cause(s) of the cracking. The issue was complicated by the presence of radiant heat tubing embedded in the slab during construction, and the absence of saw-cut joints to control cracking because of concern about damage to the tubing. Additional complicating factors included suspected deviations in the as-built slab from the construction documents, including material strength, slab thickness, and reinforcement placement parameters. The work included a review of construction documents, construction records, and material testing. The work also included the planning and execution of controlled-load measurements of crack movements in-service to gain insight in to expected long term performance.
MORE EXAMPLES TO BE POSTED SOON...